Submit this project to the proctor at the time you take Test 3.
When the problem involves hypothesis testing, use the following structure for written reports.
Hypothesis testing steps
• Step 1: State the hypotheses.
• Step 2: Summarize the data for your readers.
• Step 3: Give the value of the test statistic and the p-value.
• Step 4: Use the p-value to draw a conclusion. State the conclusion in statistical
terms: Reject Ho in favor of Ha, or retain Ho (fail to reject Ho).
• Step 5: State the conclusion in layman terms and in context of the application. Use the
p-value to state the strength of the evidence.
When a significance level is not given, then use the following guidelines and language associated
with p-value. Note that the lower the p-values, the stronger the evidence against Ho and in
favor of Ha. We go from insufficient evidence, to some evidence, to fairly strong evidence, to
strong evidence, to very strong evidence.
• p-value > .10
retain Ho – there is insufficient evidence to reject Ho in favor of Ha
• .05 < p-value ≤ .10
gray area -- decision to reject Ho or retain Ho is up to the investigators – there is some
evidence against Ho and in support of Ha
• .01 < p-value ≤ .05
reject Ho in favor of Ha – there is fairly strong evidence against Ho and in favor of Ha
• .001 < p-value ≤ .01
reject Ho in favor of Ha – there is strong evidence against Ho and in favor of Ha
• p-value ≤ .001
reject Ho in favor of Ha – there is very strong evidence against Ho and in favor of Ha
Use your TI-83/TI-84 calculator for all of these problems. You will not need any tables.
Use the Sample Test 3 Questions—Answer Key (posted in Canvas) as an example of what my
expectations are.
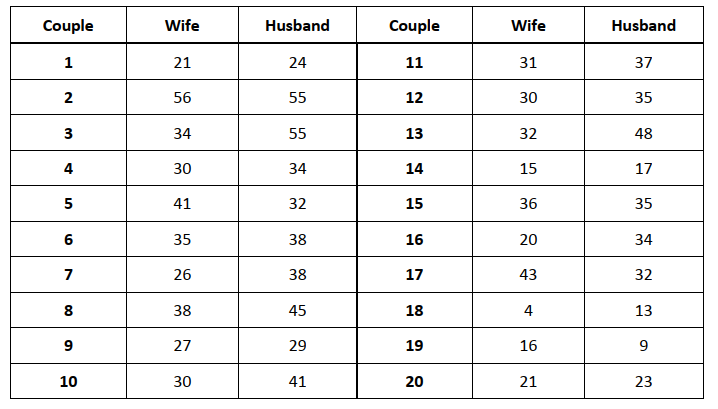
- A sociologist suspects that, for married couples with young children, the husbands watch more TV
than the wives. Twenty married couples are randomly selected and their weekly viewing times, in
hours, are recorded in the table below. Assume the population of differences between husband’s
and wife’s TV time is mound-shaped and symmetrical.
a) Do the sample results provide sufficient evidence to support the sociologist’s claim? Perform a
hypothesis test to find out.
b) If there is sufficient evidence to support the sociologist’s claim, estimate how much more TV the
husbands watch, on average, with a 95% confidence interval. Interpret.
- The data below show the sugar content (as a percentage of weight) of several national brands of
children’s and adults’ cereals. Assume the distributions of sugar content in both children’s cereals
and adults’ cereals are mound-shaped and symmetrical.
a) Does the sample data provide sufficient evidence to conclude that the sugar content in
children’s cereals is higher than that in adults’ cereals, on average? Perform a hypothesis test to
find out.
b) If you conclude that children’s cereals have more sugar than adults’ cereals, estimate how much
more with a 95% confidence interval for the difference in mean sugar content. Interpret.
Children’s cereals: 40.3, 55, 45.7, 43.3, 50.3, 45.9, 53.5, 43, 44.2, 44, 47.4, 44, 33.6, 55.1, 48.8,
50.4, 37.8, 60.3, 46.6
Adults’ cereals: 20, 30.2, 2.2, 7.5, 4.4, 22.2, 16.6, 14.5, 21.4, 3.3, 6.6, 7.8, 10.6, 16.2, 14.5, 4.1,
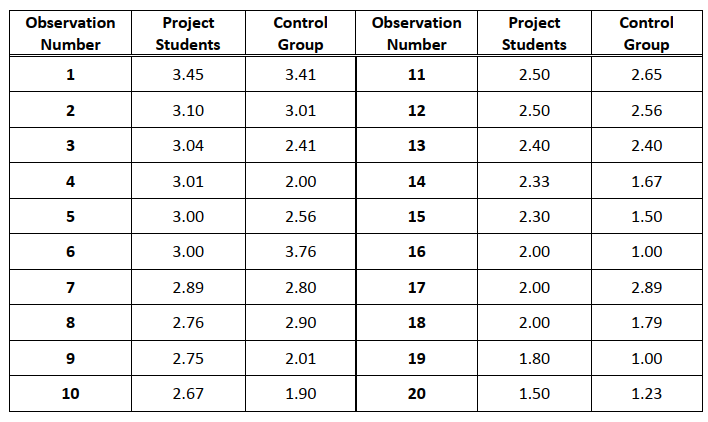
15.8, 4.1, 2.4, 3.5, 8.5, 10, 1, 4.4, 1.3, 8.1, 4.7, 18.4 - A randomly selected sample of entering college freshmen has participated in a special program to
enhance their academic abilities, and their GPAs at the end of one year have been recorded. A
group of 20 students from the same class who did not participate in the program has been selected
as a control group, and they have been matched with the experimental group by gender, age, highschool class rank, ACT scores, and declared major. The results (GPAs) are presented below. Assume
the population of differences between the project student GPA and the control group student GPA
is mound-shaped and symmetrical.
a) Can the program claim that it was successful? Carry out a hypothesis test to find out.
b) If you conclude that the program was successful, make a judgment regarding the size of the
effect of program participation on student GPAs by constructing a 95% confidence interval.
Interpret your confidence interval.
- Michelle Sayther is a fashion design artist who designs the display windows in front of a large
clothing store in New York City. Electronic counters at the entrances total the number of people
entering the store each business day. Before Michelle was hired by the store, the mean number of
people entering the store each day was 3218. Management would like to investigate whether this
number has changed since Michelle has started working. A random sample of 42 business days after
Michelle began work gave an average of 𝑋𝑋� = 3392 people entering the store each day. The sample
standard deviation was s = 287 people. Assume the population of daily number of people entering
the store is mound-shaped and symmetrical.
a) Perform a hypothesis test to decide if the average number of people entering the store each day
since Michelle was hired is different from what it was before Michelle was hired.
b) If you find that the average number of people entering the store each day since Michelle was
hired is different from what it was before Michelle was hired, estimate the average number of
people entering the store each day since Michelle was hired with a 95% confidence interval and
interpret. (Has the number of people entering the store each day increased or decreased since
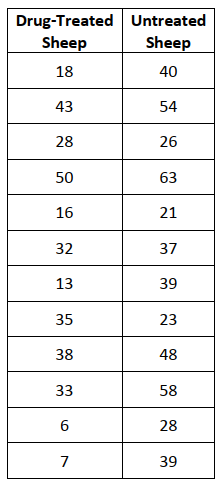
Michelle was hired, and by how much has it increased or decreased?) - An experiment was conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of a treatment for tapeworm in the
stomachs of sheep. A random sample of 24 worm-infected lambs of approximately the same age
and health was randomly divided into two groups. Twelve of the lambs were injected with the drug
and the remaining twelve were left untreated. After a 6-month period, the lambs were slaughtered
and the following worm counts were recorded. Assume the distribution of worm counts of drugtreated sheep is mound-shaped and symmetrical. Assume the distribution of worm counts of
untreated sheep is also mound-shaped and symmetrical.
c) Does the sample data provide sufficient evidence to conclude that the treatment is effective in
reducing the occurrence of tapeworm in sheep? Perform a test of significance to find out.
d) If you conclude that the treatment is effective, estimate the average reduction in tapeworm
count with a 95% confidence interval. Interpret.
- In each of the problems above, #1- #5, an assumption of normality is made about the distribution of
the population(s) from which the sample data is obtained. For each of #1 - #5, provide the page
number in the e-book where the assumption is described by the author. You will be citing page
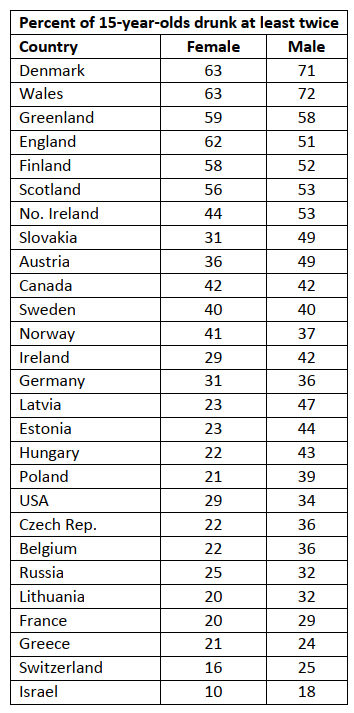
numbers from Sections 9.2, 10.1, and 10.2. - A study of the health behavior of school-aged children asked a sample of 15-year-olds in several
different countries if they had been drunk at least twice. The results are shown in the table, by
gender. (Health and Health Behavior Among Young People. Copenhagen. World Health
Organization, 2000)
a) Perform a hypothesis test to determine if there is a gender effect. That is, is there a difference
in the average percent of 15-year-old males who have been drunk at least twice and the average
percent of 15-year-old females who have been drunk at least twice? Assume the distributions
for both males and females are mound-shaped and symmetrical.
b) If there is sufficient evidence that there is a difference between average percent of 15-year-old
males who have been drunk at least twice and the average percent of 15-year-old females who
have been drunk at least twice, estimate the difference with a 95% confidence interval and
interpret your interval.
Quantitative project reasoning solutions. The following solutions have been provided to you by MyMathLab statistics experts The solutions were provided under the MyMathLab answers statistics help services.



